White spots are a common defect in hot rolled billets and large forgings and are a manifestation of hydrogen embrittlement. White spots are elongated cracks generated by hydrogen in combination with structural transformation stress and thermal stress in steel. On the transversely low-profile test piece which is polished and acid immersed, it is a hairline crack, and the white spot size is generally several millimeters to several tens of millimeters. White spots usually appear in the core of billets or forgings, usually more than 20 mm from the surface. There is also a white spotted fish-like eye nitrile called the fish eye, and the fisheye white spot usually appears on the fracture of the tensile specimen.
White spots are often found in hot-worked billets or steels and appear less in castings. Medium carbon alloy structural steel: chrome steel, chrome-nickel steel, chrome-molybdenum steel, manganese steel, chromium-manganese steel, chromium-manganese-molybdenum steel, chromium-nickel-molybdenum steel, and carbon content greater than 0.3%, chromium greater than 1%, and nickel greater than 2.5% Martensitic grade chrome-nickel steel and chrome-nickel-aluminum (tungsten), steel is most sensitive to white spots. Ball bearing steel with about 1% carbon also has a large white point sensitivity. The white point sensitivity of carbon steel is smaller than that of alloy steel, and white spots may occur when the manganese content in carbon steel is 0.7% to 1%. White spots are generally not formed in austenite, ferrite and kiltitic steels.
The higher the yield strength of the material, the more sensitive it is to white spots. Ultra-high-strength steel may also undergo hydrogen embrittlement fracture in a humid environment.
The white point sensitivity of steel is also related to the smelting method. Generally, the alkaline open hearth steel is more sensitive than the acid open hearth steel and the alkaline electric furnace steel.
Steels that are sensitive to white spots generally increase in white point sensitivity as the argon content increases. Non-metallic inclusions, particularly elongated or flaky sulfur oxides, are advantageous for forming from a point. The cooling method after forging and rolling plays an important role in the formation of white spots. The billets and forgings which are cooled faster after forging and rolling are prone to white spots.
The presence of white spots reduces the mechanical properties of the steel. Cracking may occur during heat treatment. Forgings with white spots are not allowed under any circumstances.
First, the white point fracture features
White dots are round or elliptical silver-white spots on any longitudinal macro-fracture, see Figure 7-8. The gloss of the white spots is related to the heat treatment conditions, the white spots which are not heat-treated are dark, and the silver is bright after heat treatment. The white spots darken after standing for a long time in the air.
The microscopic morphology of the white point fracture; the white point of the low-alloy high-strength steel and the alloy structural steel without heat treatment after forging is expressed as a cleavage or quasi-cleavage fracture, and quasi-cleavage is more common. The matrix other than the white point is a cleavage fracture. There is a gap between the white point and the substrate.
A dimple belt is shown in Figure 7-9. There are secondary cracks on the surface of the fracture.
For the fracture after heat treatment after forging and rolling, the white point area is a transgranular fragile floating cloud-like fracture, as shown in Figure 7-10; the corrugated shape is shown in Figure 7-11; some areas have different strip-like structures (see Figure 7-12). ), all belong to the category of quasi-cleavage fractures. There is a dimple break outside the white spot area.

Figure 7-8 White dot topography × 21
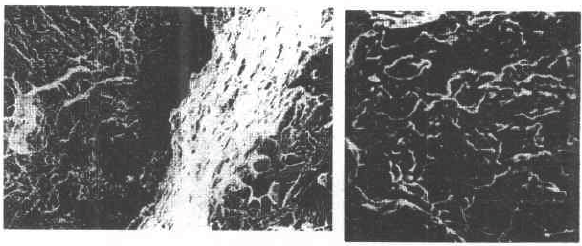
Figure 7-9 The dimple zone between the white point area and the substrate Figure 7-10 The white point area of ​​the 10CrNiMoV steel quenched and tempered slab - floating cloud

Figure 7-11 White dot area morphology after corrugation treatment - Corrugated Figure 7-12 Annealed state 5CrNiMo steel white point area shape strip x1400
Second, the fisheye type white point fracture features
The fisheye-shaped white point longitudinal macro-fracture is a silver-white round or elliptical spot with the macroscopic defect pores and slag inclusions inside the material as the core. The circular plaque area often shows a radiation structure from the center to the outside. The color, roughness and fracture mode of the round spot are obviously different from those of the parent body. See Figure 7-13. Fish-eye white spots often appear in welding, electroplating, cyanidation. Handle the tensile fracture of the test piece.

Figure 7-13 Fisheye white point
The microscopic fracture of the fisheye white point is shown as a small quasi-cleavage facet, see Figure 7-14. The fisheye crack is connected to the metal matrix in a shearing manner, with a distinct contour.
The formation of fisheye is the same as that of white spots, and its fracture characteristics are similar to those of white spots. Parts with white spots should be considered as waste, and materials containing fish eyes can generally be eliminated by heat treatment.

Figure 7-14 Microscopic appearance of fisheye
Building Wire,Pvc Building Wire,Insulated Flat Building Wire,Electrical Building Wire
TAISHAN CITY WANAN CABLE CO.,LTD , https://www.tswanan.com