The laser quenching technology and the application of the laser quenching technology are processes in which the surface of the steel material is rapidly heated by the focused laser beam to cause a phase transformation to form a martensitic hardened layer.
Laser quenching has a high power density, a fast cooling rate, and does not require a cooling medium such as water or oil. It is a clean and fast quenching process. Compared with induction quenching, flame quenching and carburizing quenching, the laser quenching hardening layer is uniform, the hardness is high (generally 1-3HRC higher than induction quenching), the workpiece deformation is small, the heating layer depth and heating trajectory are easy to control, and it is easy to automate. There is no need to design corresponding induction coils according to different part sizes like induction hardening. The processing of large parts does not need to be limited by the size of the furnace during chemical heat treatment such as carburizing and quenching, so it is gradually replacing induction hardening and chemistry in many industrial fields. Traditional processes such as heat treatment. It is especially important that the deformation of the workpiece before and after laser quenching is almost negligible, so it is particularly suitable for surface treatment of parts with high precision requirements. The depth of the laser hardened layer is generally in the range of 0.3 to 2.0 mm depending on the composition, size and shape of the part and the laser process parameters. The tooth surface of the large gear and the journal of the large shaft parts are quenched, the surface roughness is basically unchanged, and the need of subsequent machining can meet the requirements of the actual working condition. Laser condensing and quenching technology is a process in which the surface of the substrate is heated to a melting temperature by using a laser beam, and the surface of the molten layer is rapidly cooled and solidified by the heat conduction cooling inside the substrate. The obtained fused and quenched structure is very dense, and the microstructure in the depth direction is a melt-solidified layer, a phase change hardened layer, a heat affected zone, and a substrate. The laser fused layer has a deeper depth of hardening than the laser quenched layer, higher hardness, and better wear resistance. The shortcoming of this technology is that the roughness of the surface of the workpiece is damaged to a certain extent, and generally requires subsequent machining to recover. In order to reduce the surface roughness of the parts after laser fusing treatment and reduce the subsequent processing amount, a special laser fused quenching coating is prepared, which can greatly reduce the surface roughness of the fused layer. Nowadays, the workpieces such as rolls and guides of various materials in the metallurgical industry, which are laser-melted, have surface roughness close to the level of laser quenching. Laser quenching has been successfully applied to the surface strengthening of wearing parts in the metallurgical industry, machinery industry and petrochemical industry, especially in improving the service life of wearing parts such as rolls, guides, gears and cutting edges. Great economic and social benefits have been achieved. In recent years, it has become more and more widely used in the surface strengthening of parts such as molds and gears.
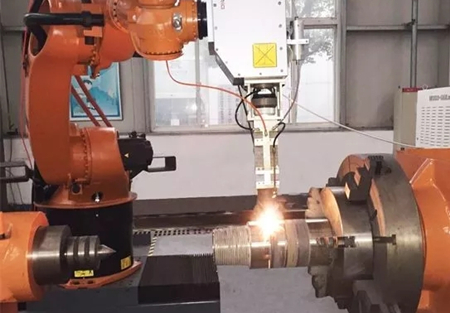
Laser quenching characteristicsQuality advantage Technical characteristics Applicable materials practical application1. Quenching parts are not deformed by laser quenching. Thermal cycle process. Medium carbon steel large shafts2. Almost no damage to surface roughness, anti-oxidation protection, thin coating, die steel, various molds3. Laser quenching, non-cracking, accurate quantification, numerical control quenching, cold work die, steel die, cutting tool4. Carbon alloy steel shock absorber for numerically controlled quenching of local, groove and groove quenching5. Laser quenching, high efficiency, no need for water or oil, etc.6. Quenching hardness is higher than that of conventional method, fine quenching layer structure, good toughness, high carbon alloy steel large rollLaser quenching equipment◠LaserQingdao ** Laser Technology Co., Ltd. 5kW CO 2 cross-flow laser GLS-VII multi-function laser processing system, can achieve various types of holes, shafts, flanges, crankshafts, laser quenching, cladding, alloying, etc. Item function.◠Large multi-function machine toolThe basic size range for laser machining machines is 5.5 meters long and Φ 2.6 meters in diameter. Special workpieces with a larger range of sizes that can be machined. This laser processing machine is a double cantilever machining system that can perform multi-station laser processing.◠Six-axis four-link CNC systemThe machine is equipped with a six-axis four-link CNC system for precise laser machining of complex shaped workpieces.Laser quenching effectHardness distribution curve of laser quenching layer Hardness distribution of laser quenching layerLaser quenching industrial application examplesLaser quenching technology can surface strengthen various guide rails, large gears, journals, cylinder inner walls, molds, dampers, friction wheels, rolls, and roller parts. Suitable materials are medium and high carbon steel and cast iron. Application examples of laser quenching: laser quenching and strengthening cast iron engine cylinders, the hardness of HB230 is increased to HB680, and the service life is increased by 2~3 times.
Brass sink faucet is heavily used every day between brushing your teeth and washing your hands multiple times. Choose a tub faucet that is not only reliable and water efficient, but also fits your style and budget. We have the latest styles of sink faucets to choose from. Stainless steel bathroom faucets are spot-proof. In addition to resisting spots and fingerprints, the matte black Brass sink faucet enhances durability.
Brass Faucet,Brass Kitchen Faucet,Brass Bathroom Faucets,Brass Shower Fixtures
JIANGMEN MEIAO KITCHEN AND BATH CO.,LTD , https://www.meiaogroup.com