Recently, the team of Xiao Jianping, a researcher of the Research Group of Theoretical Catalytic Innovation Special State of the State Key Laboratory of Catalysis, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, teamed up with Professor Xiao Fengshou of Zhejiang University and Wang Liang, a team of researchers, to make new progress in the study of one-step synthesis of ethanol from syngas .
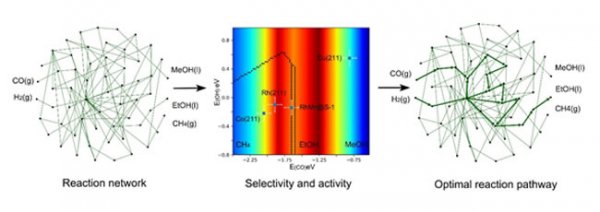
Ethanol is an important chemical and fuel. Efficient and highly selective direct production of ethanol via synthesis gas is currently a hotspot in the field of energy research. If the catalyst is too reactive or too weak, the selectivity of by-products will be too high, so it is also difficult to directly produce ethanol from syngas. A thorough understanding of the reaction mechanism of synthesis gas conversion is of great significance for the subsequent improvement of catalyst activity and the search for non-noble metal catalysts. There are dozens of intermediates and transition states and thousands of reaction paths in the synthesis gas conversion process, and the traditional theoretical methods cannot well understand this process. Based on this, the team of Xiao Jianping has developed a new method of reaction path research and product selectivity analysis, which can simplify the adsorption energy of dozens of intermediates and transition states to two dimensions-the adsorption energy of CO and OH, and to This is to describe the selectivity of different catalysts to products (such as the two-dimensional reaction phase diagram above), and to understand and guide the design of the catalyst. This method can also integrate thermodynamic and kinetic effects to automatically search for the optimal reaction path for ethanol production.
In the synthesis gas conversion process, if the CO molecule and the catalyst (such as pure Rh, Co catalyst, etc.) are too strongly combined, the carbon-oxygen bond is basically broken, and then methane is selectively obtained; if the CO and the catalyst (such as the Cu catalyst) are combined Too weak, the carbon-oxygen bond cannot be broken at all, so only methanol can be obtained. Only when there is a very small energy window between CO and catalyst, the intermediate (CHx *) after CO dissociation and undissociated CO * / CHO * can coexist to have better ethanol selectivity. Theoretical calculations show that the coupling of CH2 * and CO / CHO * intermediates is the most critical step. The MnOx structure and the restricted environment provided by the molecular sieve affect the electronic structure of the Rh atom at the interface (near MnOx), making RhMn @ S The -1 catalyst happens to fall in this range, and ultimately allows CH2 * and CO * / CHO * intermediate substances to coexist in large quantities, resulting in higher ethanol selectivity. This work provides new ideas for the design of catalysts for the preparation of ethanol with highly selective synthesis gas.
Related results were published in Chem. This work was supported by the National Major R & D Program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the key deployment project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the "Xingliao Talent Program" in Liaoning Province.
As
the name suggests, diaphragm metering pump using a special design and
processing of flexible diaphragm instead of the piston, under the action
of the drive mechanism to achieve reciprocating motion, complete the
suction - discharge process. Due
to the segregation of the diaphragm, the isolation between the metering
fluid and the driving lubrication mechanism is realized in the
structure. High-tech structural design and the selection of new materials has
greatly improved the service life of the diaphragm, coupled with
excellent corrosion resistance of composite materials, diaphragm
metering pumps become the main application of fluid measurement pump
type.
In
the diaphragm-type metering pump family members, the hydraulic
diaphragm metering pump as a result of the use of hydraulic oil evenly
drive the diaphragm, to overcome the mechanical direct drive mode under
the pump diaphragm too concentrated shortcomings, to enhance the
diaphragm life and working pressure ceiling. In
order to overcome the single diaphragm metering pump may occur due to
damage caused by the diaphragm damage, and some metering pumps equipped
with a diaphragm breakage sensor to achieve the diaphragm when the
automatic chain protection; with double diaphragm structure of the pump
head to further improve its safety Sex, suitable for security protection is particularly sensitive to the application.
As a kind of diaphragm type metering pump, the electromagnetic driven
metering pump generates the pulsating driving force with the
electromagnet, which saves the motor and the speed change mechanism,
makes the system compact and compact, it is an important branch of the
small range low pressure metering pump.
Precision metering pump technology has been very mature, the fluid metering capacity of up to 0-100,000l / h, working pressure up to 4000bar, the scope of work covers all areas of industrial production requirements.
If you want to buy Mechanical Diaphragm Metering Pump, Solenoid Diaphragm Metering Pump(electromagnetic metering pump), Water Treatment Dosing Pump, Plastic Chemical Diaphragm Metering Pump, please contact us.
Diaphragm Metering Pump,Mechanical Diaphragm Metering Pump,Solenoid Diaphragm Metering Pump,Plastic Chemical Diaphragm Metering Pump,Water Treatment Dosing Pump,Electromagnetic Metering Pump
Zhejiang Ailipu Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.alipu.com